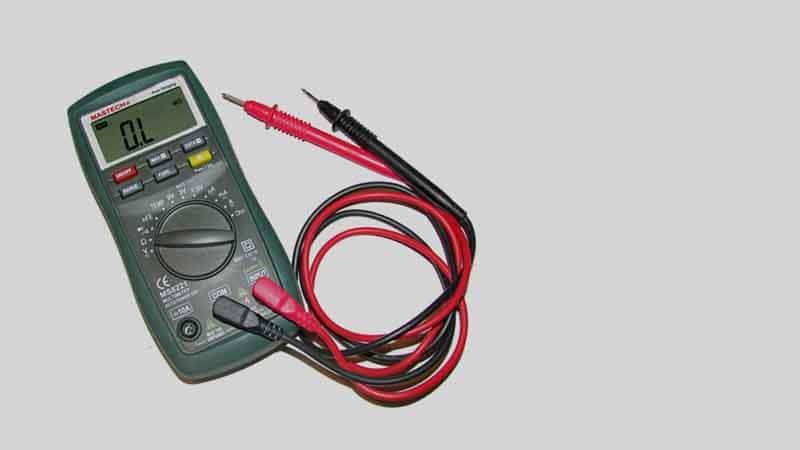
A multimeter is a portable digital tool that you can use to test electronic equipment for any electrical related problems. Basically, it measures various aspects of the equipment and turns the measurements into analog information. These measurements are transformed into a digital signal that can be seen on the multimeter’s display screen.
Basic Features
The types of measurements you can see on the multimeter include DC voltage, AC voltage, current, temperature, resistance, capacitance, and frequency. However, there are different types of multimeters, so don’t expect every model to give you all this information. The standard three measurements you should get from a multimeter are current, voltage, and resistance. If you want any of the other measurements, then look for special multimeters that offer those measurements too.
Most people use a multimeter to test the voltage of a circuit. This is important for figuring out how much voltage is in a particular power source. DC voltage and AC voltage are what you’ll want to concern yourself with the most. For instance, if you want to test the direct current of a circuit, you would do the following:
Testing a DC Circuit and AC Circuit
Go to the meter and find the right terminals. The test leads must be installed into the terminals. You’ll notice each lead is color-coded as red and black. The port which has the ∨Ω symbol receives the red lead and the port labeled COM receives the black lead. Now activate your multimeter device. The selector switch must get moved to the letter “V,” which stands for voltage. Make sure it is the V with the dashed line and solid line next to it.
The test leads should now be connected to the DC circuit. Match the red lead up with the positive point of the circuit and the black lead with the negative point. The negative being the circuit ground, of course. After a couple of seconds or less, the display screen should give you a new reading. What you see is the amount of voltage of the circuit. This could be the voltage of the battery in some cases.
If you put the leads on the wrong points, then your display screen will show a reading of a “-“ negative symbol. Remove the leads and put them on the proper points as described above and you will fix this problem. Sometimes you may not see any reading at all. Make sure your leads are connected properly and that you have the proper setting chosen for the multimeter. If that doesn’t work, then your circuit either needs to be turned on, or it is dead.
To test an AC circuit, a lot of the same steps will apply. The red lead goes with the ∨Ω port and the black lead goes with the COM port. Activate your multimeter device and position the selector switch next to the letter “V,” but make sure it is the V that has the wave next to it. Lead placement is not important here because it is an AC circuit. However, you should learn the potential readings of the conductors just in case.
Read also:
- How to Test Diode using an Analog Multimeter
- What Happens if a Diode is Reversed?
- 10 Different Types of Diodes and their functions
Average Multimeter Price
Your average digital multimeter is priced between $50 and $400. They are not terribly expensive. The only reason you would need a more expensive one is if you want to get additional measurements for other things besides current, voltage, and resistance. A professional electrician or electronics expert would definitely have a top-quality multimeter. But if you’re a hobbyist or handyman, then you can settle for a $50 to $150 digital multimeter, and it should suit you just fine.